Planned Preventative Maintenance
PLANNED PREVENTATIVE MAINTENANCE
How to plan preventative maintenance?
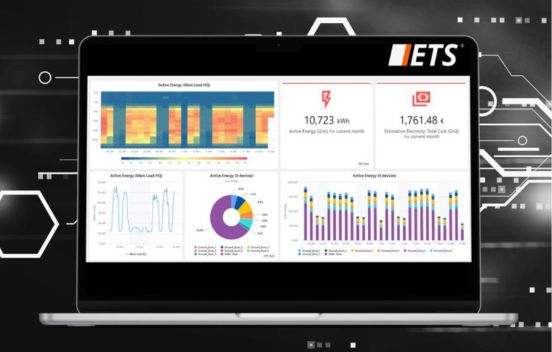
Planned preventative maintenance (PPM) enables you to effectively minimise reactive maintenance and ensure the longevity of your buildings and assets. It not only enhances the energy efficiency but also empowers your building assets. Planned Preventative Maintenance (PPM) is a structured operational plan that when applied and administered correctly, ensures that building services plant, equipment and controls operates effectively, efficiently, enhances service longevity, minimises service disruption, environmental impact, and ensures that a building is compliant with requirements.A structured maintenance planner and procedures ensures that all personnel involved in the the delivery of maintenance understand fully the requirements, it adheres to appropriate frequencies and does not expose the building to service failure, poor environmental conditions, health & safety risks or failure to fulfil statutory obligations. Applied correctly, plant will be maintained at it’s most optimal performance and energy efficiency, comfort and performance will be sustained. Effective delivery also helps to extend the lifespan of equipment and prevent degradation and failure. Energy & Technical Services has developed numerous maintenance initiatives, specifications, tenders and we monitor the delivery on behalf of building operators and owners. As energy management practitioners energy efficiency, particularly in maintenance is core to how we promote and encourage the delivery. Contact to grab this opportunity to maximise operational efficiency!
From building design and inception through to installation and commissioning, often plant, equipment and systems do not perform as intended, which can be down to design and limitations versus expectations, a change in use and application, poor maintenance, inadequate control strategies or from a low level of technical knowledge and capability to operate as prescribed. Auditing plant and maintenance performance periodically ensures that the building, plant, systems and controls are maintained and operating optimally and correctly and provides early warning indicators when tolerances and services are not met, which can often cause performance gaps with energy and operational efficiency.
Assessing PPM strategies and monitoring delivery of maintenance is critical to the overall process and ensures that those teams or organisations responsible for delivery have the knowledge, support, technical skill in which to deliver their obligations. We work with many of our clients maintenance teams to support, improve standards, and educate whilst ensuring energy and optimisation is core to the overall strategy and performance. Unlock your energy potential today!
Our engineering and technical consultants offer plant and equipment asset surveys, plant replacement strategies & plans aligned with condition, age and performance to ensure that when coupled with structured PPM delivery, the overall asset strategy is dynamic, responsive and reflective to accommodate contemporary and future development and needs of the building and occupants. It allows our clients to plan the necessary investment required to ensure that each element of the building operates at its optimum level. It is critical to keep in mind that PPM covers all aspects of planned maintenance, not just preventative maintenance.
Periodic surveys & audits of plant condition, maintainability and performance is critical to the overall process. Adopting this independently through Energy & Technical Services ensures that an appraisal is objective, transparent and effective to gain a full understanding of performance capability and limitations, as well as providing critical early warning indicators where issues are likely to arise continually under review.
A PPM programme should prevent a building from experiencing unexpected plant failure and mitigate compliance risks. However, you should not solely depend on your maintenance provider to alert you of potential issues. You should still review the quality of the maintenance undertaken, ensure compliance checks are being carried out regularly, and verify that plant and equipment is operating efficiently.
Building owners / occupiers may be unaware of the potential issues that may arise unexpectedly from inefficient and poorly maintained equipment. Conducting a PPM audit will highlight any potential issues with your current maintenance schedule. It will not only provide insight into the quality of service received from the maintenance contractor but also if works are being carried out to avoid equipment failure. Most importantly, a PPM audit will highlight if plant equipment is being maintained to legal conformance standards as well as highlighting the condition and remaining life expectancy of the systems.
A PPM audit will encompass a review of the scheduling, frequency, compliance and conformance to specification of the PPM services being undertaken by maintenance contractors as well as identifying persistent service failure and faults. It will also provide a life cycle analysis of equipment and a dilapidations, which is important information to help building managers to budget for potential repairs or replacements.
One of the most common issues with PPM is remedial works or tasks not being undertaken, or that evidence of works is not available and not documented correctly. It is important to use an impartial adviser that will be able to review the maintenance regime at your site.
PPM can be splitted into two types: time-based and condition-based maintenance.
Time-based preventative maintenance
Time-based preventative maintenance involves carrying out maintenance tasks on a fixed schedule, according to a predetermined calendar. The maintenance schedule for an asset, equipment, plant or building fabric is dependent on maintenance activities and the frequency of execution. These frequencies can be determined by warranties, supplier instructions, legislation or experience. For example, an annual inspection of a heating unit, cleaning its filters every 2 years, and replacing its filters every 5 years, is a time-based maintenance. However, relying solely on time-based maintenance can result in reactive maintenance if the asset’s actual condition is not taken into account. It can also lead to maintenance being performed too early or unnecessarily, if the asset’s condition is better than expected.
Condition-based preventative maintenance
Condition-based preventative maintenance is a highly effective method for predicting potential asset failure and preventing it through timely maintenance. This approach is the most effective for assets that can provide real-time updates to the maintenance system, like IWMS, CAFM, CMMS and EAM. By continuously monitoring an asset’s condition, maintenance can be performed just in time, thereby reducing costs and preventing reactive maintenance efforts that are often associated with asset failure. If, for instance, the temperature of your air conditioning installation exceeds a pre-determined threshold value, a preventive maintenance activity will be generated to prevent any failure. Similarly, if the operating hours exceed a predetermined limit, the next maintenance activity will be automatically scheduled at the appropriate time, which gives the best efficiency.
If you have any questions or would like to discuss further what you should be doing, ETS is here and willing to help.
Building Optimisation & BMS Controls during the Summer
Developing a Preventative Maintenance Plan – Top 10 Non-Conformance Issues
The Importance of Planned Preventive Maintenance (PPM) Audits
Why Planned Preventative Maintenance (PPM)?
The longevity of assets
Planned Preventative Maintenance (PPM) is a structured operational plan that when applied and administered correctly, ensures that building services plant, equipment and controls operates effectively which leads to a long-term win.
early warning indicators
The system provides early warning indicators when tolerances and services are not met, and it avoids performance gaps happening with energy and operational efficiency.

Better energy efficiency
Don’t miss out on the full potential that these advancements can offer due to ineffective connectivity between systems.